Salts containing ortho-phosphite anions have now been synthesised by mechanochemically reducing phosphate compounds. Researchers says ortho-phosphite is synthetically versatile, making it an attractive alternative to toxic and flammable white phosphorus, which is the current starting point for a range of phosphorus compounds.
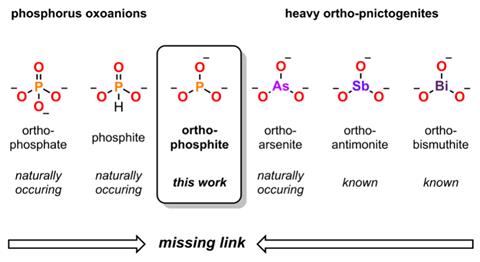
Many phosphorus oxyanions exist, such as phosphate (PO43-) and phosphite (HPO32-). Yet, the ortho-phosphite (PO33-) anion – where a central phosphorus atom is connected to three singularly charged oxygen atoms – has remained elusive, despite teachers often using it as an example to help explain Lewis structures to students.
Researchers from the US have now plugged this gap by synthesising various group 1 ortho-phosphite salts, adding to the set of heavier group 15 trioxyanions currently known.
Ball milling phosphate sources with sodium, potassium or caesium salts for up to 36 hours led to a mixture of reduced phosphorus species. Solid state NMR and Raman spectroscopy revealed key peaks for the ortho-phosphite anion, which closely matched calculated estimates. As a result, the researchers were able to show ortho-phosphite salts were a major component of the mixture, along with phosphate, hypophosphate (P2O64-) and phosphide (P3-) compounds.
Hydrolysis of ortho-phosphite led to phosphite, a useful phosphorylating agent. Reacting the crude mixture with trimethylsilyl chloride generated tris(trimethylsilyl)phosphite, which can act as a precursor to many organophosphorus compounds. Attempts to alkylate ortho-phosphite were successful, but products were difficult to purify from the mixture, leading to low yields.
The researchers say ortho-phosphite’s versatility as a reagent could allow chemists to generate valuable organophosphorus compounds without needing to use white phosphorus, which is currently the go-to reagent. The team is now further developing the synthesis of ortho-phosphite and exploring the full scope of its reactivity.
References
P Löwe et al, ACS Cent. Sci., 2025, DOI: 10.1021/acscentsci.5c01595













No comments yet