All articles by Kira Welter
-
 Research
ResearchNew electron diffraction strategy could make it easier to study solvated organic microcrystals
The approach combines carbon liquid cells and rapid data acquisition to study solvated molecules at room temperature
-
 Research
ResearchPosition of flask on magnetic stirrers can drastically affect reproducibility of experiments
Comprehensive examination reveals improper siting of reaction vessels can affect catalyst formation, alter nanoparticle formation and change yields
-
 Research
ResearchCatenane with tuneable mechanical chirality created
The chirality of a compact cationic catenane can be controlled using chiral sulfonate anions
-
 Research
ResearchMercury-free electrochemical lithium isotope separation could fuel a fusion future
Vanadium oxide pores selectively sequester sieve lithium isotopes
-
 Research
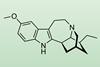
ResearchTotal synthesis of anti-addictive alkaloid in just seven steps
A streamlined synthesis of the psychoactive compound ibogaine could open up new opportunities in the treatment of drug addiction and depression
-
 Research
ResearchComputer simulations shed light on how material can shrink when heated
New theory offers insights into the origin of the very low and negative thermal expansion observed in cordierite
-
 Research
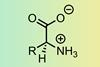
ResearchIncorrect pKa values have slipped into chemical databases and could distort drug design
Confusion in zwitterionic compounds leads to misrepresented data in widely used repositories such as ChEMBL
-
 Research
ResearchElectrochemical series for materials makes predicting oxidation states easy
Machine-learning trained model could open up new opportunities in materials discovery
-
 Research
ResearchChemical ‘waves’ used to encode words as Morse code
A controllable, oscillating reaction has been used to generate waves of different forms for information transduction
-
 Research
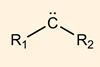
ResearchHarnessing carbene reactivity with light
Two-step photocatalytic strategy produces metal carbenes easily and safely
-
 Research
Research‘Late-stage saturation’ could improve drugs' effectiveness
Approach turns flat aromatic structures into three-dimensional saturated molecules with improved medicinal properties
-
 Research
ResearchNon-antibiotics with antibacterial activity could help in the fight against antimicrobial resistance
New analysis shows that non-antibiotic drugs kill bacteria through mechanisms that differ from those of conventional antibiotics
-
 Research
ResearchAnswer found for why like-charged particles sometimes attract each other
It’s not just opposites that always attract as new research confirms an observation that has puzzled scientists for over 80 years
-
 Research
ResearchWatching molecular ions transform in real time
A new method that combines ultrafast electron diffraction with multiphoton ionisation has captured the dynamics of a cation in the gas phase for the first time
-
 Research
ResearchFleeting phenomenon of water autoionisation pinned down by neural network simulations
Modelling sheds light on a process that has been known for over a century but was tricky to understand
-
 Research
ResearchChemical oscillator’s tick-tock action catalyses reaction regular as clockwork
Small molecule oscillator can catalyse Knoevenagel condensation periodically without affecting the oscillation
-
 Research
ResearchPhotophysical oxidation plays newly discovered role in atmospheric chemistry
Process is likely to be a general mechanism in tropospheric chemistry, especially at low altitudes
-
 Research
ResearchMetallic hydrogen and diamonds may have been made from plastics
A combination of x-ray diffraction experiments and simulations suggests that an intense laser can transform polystyrene
-
 Research
ResearchRecycling wind turbine blades by breaking them down into their constituent chemicals
Thermoset plastics that normally end up in landfill can be selectively depolymerised using a ruthenium catalyst
-
 Research
ResearchMechanochemically accelerated sublimations used to separate chiral molecules
New technique combines ball milling with NMR to monitor sublimations in real time