Google’s new deep learning model can predict the effect of small changes to DNA sequences up to one million base pairs in length and is particularly good with non-coding DNA, which has proven especially difficult to understand. The artificial intelligence (AI) tool – called AlphaGenome – offers researchers a way to better understand the human genome and may help scientists develop treatments for disease.
AlphaGenome is ‘a foundational, high-quality tool that turns the static code of the genome into a decipherable language’
Robert Goldstone, Francis Crick Institute
Small variations in the human genome can have a big impact on a person’s health, causing genetic disorders like cystic fibrosis or certain cancers. Most changes occur in the genome’s non-coding regions that make up 98% of the total DNA. These regions influence the expression of genes, rather than coding for proteins, and alterations can often have a range of biological effects, making it hard to predict their impact.
AlphaGenome, developed by Google DeepMind, can predict the molecular impact of single base pair variations across whole DNA sequences up to a million base pairs in length. This builds on Google’s earlier model, AlphaMissense, which was only able to understand the effects of variations in the coding region of DNA sequences.
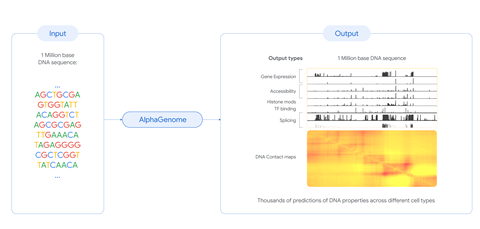
The new model – trained on human and mouse genome data – takes a DNA sequence as an input and gives predictions on various genetic signals that relate to specific biological functions. This includes gene expression, DNA’s accessibility to proteins and where gene splicing occurs.
‘The key [benefit] is that you can introduce a mutation to the sequence, changing for example a C [base pair] to a T, and then use the model to compare these differences,’ says Google DeepMind researcher Žiga Avsec.
What do we mean when we say AI?
Artificial intelligence (AI) is an umbrella term often incorrectly used to encompass a variety of connected but simpler processes.
AI is the ability of machines and computer programmes to perform tasks that typically only humans could do, such as reasoning, responding to feedback and decision making.
Generative AI is a newer variant of AI that analyses and detects patterns in training datasets to generate original text, images and videos in response to requests from users. ChatGPT, Microsoft Copilot, Google Gemini and more recently X’s Grok are all examples of chatbots that use generative AI.
Neural networks are an interconnected array of artificial neurons, akin to biological brains, that identify, analyse and learn from statistical patterns in data.
Machine learning is a subset of AI that allows machines to learn from datasets and make predictions based on new data, without programmers explicitly asking it to do so. Machine learning models improve their performance as they receive more data.
Deep learning is an enhanced type of machine learning that uses neural networks with many layers to analyse complex data from very large datasets. Applications of deep learning include speech recognition, image generation and translation.
Large language models or LLMs are a type of deep learning trained on large amounts of data to understand and generate language. LLMs learn patterns in text by predicting the next word in the sequence and these models are now able to write prose, analyse text from the internet and hold dialogues with users.
AlphaGenome matched or outperformed other state-of-the-art models in 25 out of 26 tasks predicting the effects of genetic variations. The team were also able to simulate known DNA mutations responsible for a type of leukaemia, predicting the same results as those observed in the lab.
‘Previously, the field required separate models for separate tasks,’ says Avsec, adding that earlier models also often had a trade-off between sequence length and resolution. ‘AlphaGenome unifies these under one roof.’
Natasha Latysheva, a senior research engineer at DeepMind, explains that AlphaGenome may help improve fundamental knowledge about the genome, improve understanding of rare diseases and cancers or help scientists design new DNA sequences to treat specific conditions.
AlphaGenome adds to the collection of other AI tools developed by Google DeepMind, which includes the 2024 Nobel prize winning AlphaFold that predicts the 3D shape of proteins. Pushmeet Kohli, who led the work, explains that ‘the genome is the recipe and understanding the effect of changing any part of the recipe is what AlphaGenome looks at’.
AlphaGenome turns genetic code into ‘decipherable language of discovery’
Robert Goldstone, head of genomics at the Francis Crick Institute in the UK, believes that AlphaGenome is ‘a foundational, high-quality tool that turns the static code of the genome into a decipherable language for discovery’, but warns that it ‘is not a magic bullet for all biological questions’.
Despite the improvements, AlphaGenome still has a number of limitations. Like other models, it struggles to predict the influence of genetic alterations that are more than 100,000 base pairs apart and can only make predictions about DNA sequences from the cell types used to train the model – namely human and mouse.
Another issue is interpreting results from the model, explains Jian Zhou, a genomics machine learning researcher at the University of Chicago in the US. ‘Even when the model makes accurate predictions, it does not always directly inform us of the underlying biological processes,’ he adds.
Google DeepMind released a preview of the model for non-commercial research in June last year. Since then, Kohli explains that nearly 3000 scientists in 160 different countries have used AlphaGenome, submitting around 1 million requests each day.
He hopes that ‘AlphaGenome will continue to be a valuable resource for the scientific community and help scientists better understand genome function and disease biology, and ultimately drive new biological discoveries and … new treatments’.
References
Z Avsec et al,Nature, 2026, DOI: 10.1038/s41586-025-10014-0













No comments yet