Rotational restriction
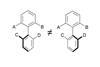
A simple method for transferring point chirality to axial chirality
The idea of atropisomerism is not immediately obvious. This form of chirality arises when two forms of a molecule are differentiated by hindered rotation around a single bond, and gets its name from the Greek atropos (not turning). Chirality at a single atom (point chirality), is a conceptual challenge in its own right. But as a foundational tenet of chemistry, it is something students soon become familiar with. Atropisomerism is not only encountered less often, but is visually a more challenging concept: restricted rotation around a single bond is not something that can be definitively drawn on paper. We must mentally acknowledge that the bond in question cannot rotate. As a consequence, pairs of distinct, conformationally stable compounds are often viewed as one.