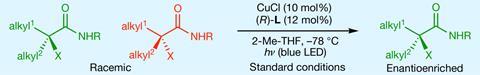
A new light-activated catalyst breaks and resets carbon–halogen bonds to convert racemic mixtures into enantiomerically enriched products. It is the first time that such a technique has targeted bonds involving heteroatoms. The process could streamline the synthesis of chiral pharmaceuticals, where precise enantiomer control is essential for biological activity.
‘Others have used photochemistry to deracemise compounds through the cleavage of carbon–carbon and carbon–hydrogen bonds,’ explains Gregory Fu from the California Institute of Technology, US. However, these approaches struggle with alkyl halides due to the strength of the carbon–halogen bonds, says Fu, who led the work along with computational chemist Peng Liu, from the University of Pittsburgh, US. ‘To our knowledge, this study demonstrates for the first time the viability of photoinduced deracemisation through the cleavage of other bonds,’ adds Fu.
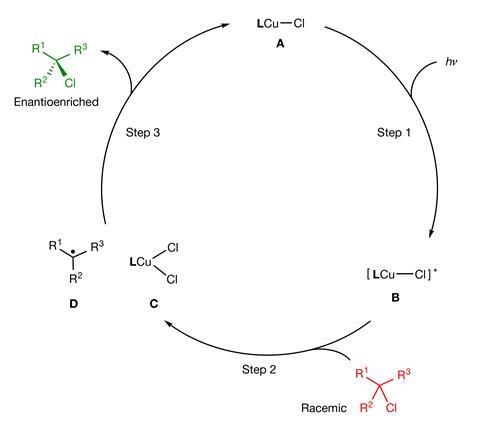
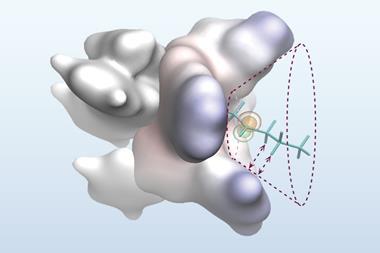
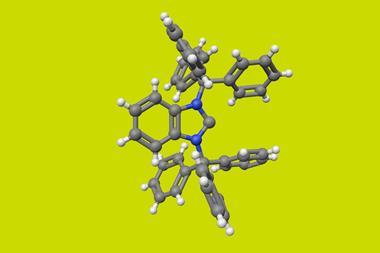
The new catalyst features a copper chloride unit bound to a bulky, chiral phosphine ligand that modulates its reactivity. When activated by light, the excited catalyst engages in a single electron transfer reaction with an alkyl halide substrate, breaking its carbon–halide bond and generating a radical intermediate. Chloride transfer from the copper complex to the radical then completes the process, with the chiral phosphine ligand directing the stereochemical outcome of the reaction towards the desired single-enantiomer product.
The researchers demonstrated the method’s versatility by applying it to various alkyl halides, achieving high yields and enantioselectivity. ‘This is a very synthetically useful way to make a broad range of challenging stereogenic centres in a highly enriched fashion’, says Liu. ‘Once we can access these chiral alkyl halides, we can easily convert those alkyl halides into many different types of carbon–heteroatom bonds.’
‘The mechanistic and computational studies methodically elucidate all steps of the transformation,’ comments Eric Ferreira, an expert in transition metal catalysis from the University of Georgia, US, who was not involved in the project. He describes the work as ‘remarkable’ and notes that the concept ‘appears generalisable, in principle, for enantioselective halide atom transfer’. Ferreira adds that ‘further expansions of substrate classes appear within reach through catalyst modifications’.
References
F Zhong et al, Nature, 2025, 640, 107 (DOI: 10.1038/s41586-025-08784-8)












No comments yet