Cocatalysts on the outside and inside of hollow spheres trigger photocatalytic carbon dioxide reduction to syngas
Developing new ways to recycle waste gases into useful resources is becoming increasingly important, but until now, scientists have struggled to turn carbon dioxide into useful products with a good yield. Now, researchers in China have created a new photocatalyst with a hollow spherical structure that converts waste carbon dioxide into syngas, a highly valuable chemical feedstock – and by adjusting the metal composition on the outside of the spheres, the reaction can be fine-tuned to give the most optimal yield of gases.
Syngas, an abbreviation for synthesis gas, is a mixture of carbon monoxide and hydrogen. Syngas is important in industry for producing valuable chemicals such as ammonia and methanol, as well as for generating natural gas and constructing liquid hydrocarbons via the Fischer–Tropsch process. Industrial chemists typically make syngas using processes like gasification and steam reforming, but these methods are strongly endothermic and require temperatures above 700°C.
Scientists have reduced carbon dioxide using photocatalysis before, but the catalysts suffer from huge problems – including significant electron–hole recombination, which halts the reaction, and an undesirable ratio of carbon monoxide and hydrogen products – that make them unsuitable for use on an industrial scale. Jinlong Gong and his team at Tianjin University set out to develop a catalyst for carbon dioxide reduction that avoids these problems. By loading oxidative MnOx particles on the inside of a hollow TiO2 sphere, then depositing a reductive copper–platinum alloy on the outside of the sphere, the team created a spatially separated tuneable cocatalyst structure that makes electron–hole recombination impossible.
‘Unlike previous ones, our cocatalyst structure is completely separated by a TiO2 shell, enabling electrons and holes generated by TiO2 to flow in opposite directions, which greatly supresses charge carrier recombination,’ Gong tells Chemistry World. Irradiation by solar light causes TiO2 to generate electron–hole pairs, which separate on the oppositely charged surfaces either side of the hollow spherical shell. ‘Holes are collected by oxidation cocatalysts on the inner surface and are consumed by a sacrificial agent, whereas electrons are enriched by the reduction cocatalysts on the outer surface, which drive the carbon dioxide reduction and hydrogen evolution reactions,’ he continues.
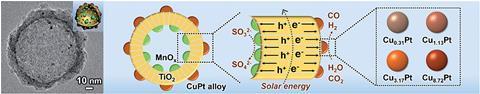
‘This tailored structure is a notable improvement over randomly located co-catalysts,’ says Gerardo Colón, a researcher at the Materials Science Institute of Seville, Spain. ‘In addition, by tuning the copper composition in the copper–platinum alloy, it’s possible to control the carbon monoxide to hydrogen ratio in the syngas mixture – the copper content in the alloy affects the reaction energetics by changing the carbon dioxide activation and carbon monoxide desorption energies,’ he says. A higher copper content inhibits hydrogen evolution and results in a greater proportion of carbon monoxide, and a higher platinum content does the opposite.
However, Colón believes that despite the big improvements over previous methods, the cocatalysts are still far from industrial use. ‘The carbon dioxide conversion efficiency is still in its infancy. Much work remains to bring this technology to reality, but the reported carbon dioxide reduction yield of 0.108% is a promising starting point,’ he says. Gong agrees, and says that one of the most important challenges they face is improving the material’s light absorbance, which will increase the yield in turn.















No comments yet