Scientists have shown that bacterial ribosomes can incorporate cyclic beta amino acids into polypeptides. By expanding the set of monomers that nature’s translation machinery is understood to work with, the work could help scientists produce exotic proteins or peptide-based drugs.
The number of alpha amino acids that a ribosome will combine has already grown from nature’s 20 amino acids, to over 150 synthetic amino acids. Now, researchers led by Michael Jewett at Northwestern University in the US have added cyclic beta amino acids to the club. Cyclic beta amino acids are more rigid than alpha amino acids so result in polypeptides with different helix geometries or turning capabilities to those found in nature.
‘This is an excellent example of how chemistry can be used to probe the function and flexibility of biological systems,’ says structural biology researcher Sabine Schneider from Ludwig Maximilian University of Munich in Germany. ‘This might ultimately lead to the production of biomolecules with novel properties.’
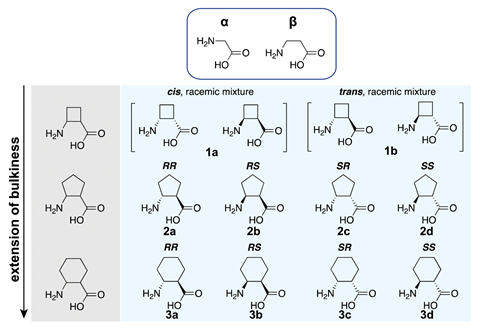
Jewett’s team added beta amino acids and charged tRNA to ribosomes in vitro then used a commercial protein synthesis platform to enable translation. However, these cyclic beta amino acids initially proved awkward for the ribosomes to work with as, compared to alpha amino acids, they have an extra carbon linkage. ‘The natural ribosome has evolved over hundreds of millions of years to molecularly transform and polymerise alpha amino acids,’ explains Jewett. ‘What we found is that the ribosome is capable of polymerising these cyclic beta amino acids, but it’s inefficient.’ So the team included an additional elongation factor that the translation apparatus normally uses, called elongation factor P, which successfully accelerated the process.
‘How the ribosome works, and identifying its limits for polymer synthesis have been long-standing fundamental questions,’ comments Ryan Mehl, who works on genetic code expansion at Oregon State University in the US. ‘This work adds to the growing evidence that understanding how elongation factor P tunes ribosome function could be the magic key to unlock new levels of polymer synthesis.’
The researchers are now exploring what other monomer classes the ribosome will work with. ‘Could we move beyond this set of beta carbons to get to a broader set of backbone-extended monomers?’ asks Jewett. ‘How far can the ribosome go before it really doesn’t work?’
References
This article is free to access until 29 June 2020
J Lee et al, Chem. Commun., 2020, DOI: 10.1039/d0cc02121k






No comments yet