Researchers have discovered a force-induced carbon–carbon bond rupture that follows three different mechanistic pathways at the same time – a first for mechanochemistry and possibly for organic chemistry, according to the study’s leader Guillaume De Bo from the University of Manchester, UK. Tuning the bond’s polarity influences which mechanism becomes dominant, which could help chemists make self-healing materials or plastics that break down under mechanical strain.
De Bo and his team were studying how ultrasound fractures a polymer with a built-in mechanophore, a molecular unit that breaks upon mechanical activation. The activation liberates a carbene that can catalyse further chemical reactions. ‘However, we failed to observe any catalytic activity,’ De Bo says. ‘This made us wonder that maybe the bonds were breaking in an unexpected fashion.’
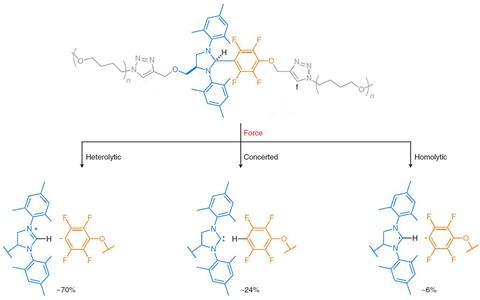
Covalent bonds can break in three different ways, according to what happens to the electrons in the bond. The electrons can be shared equally between the atoms (forming two radicals), or unequally (forming ions) or they can instantly create new bonds (forming neutral species). The researchers were expecting a concerted bond cleavage between the central imidazolidine and the tetrafluoroaromatic unit, producing a neutral carbene, but instead they observed the ionic products of a heterolytic mechanism. ‘These heterolytic scissions are less frequent in polymer mechanochemistry,’ explains De Bo. Additional experiments showed even more unexpected products – among them small amounts of the carbene and traces of free radicals.
‘It is rare to see categorically distinct mechanisms coming out of the same conditions for C–C bond scission,’ says AJ Boydston, an expert in polymer mechanochemistry at the University of Wisconsin-Madison, US. ‘[Such] subtle differences in mechanophore designs are hard to detect in bulk experiments,’ he adds.
‘The analytical work in this report was not necessarily routine,’ Boydston says. Indeed, De Bo’s team carried out deuterium labelling experiments and computational work to identify the different bond cleavage pathways. ‘The computational work sheds light on how to […] develop predictive capabilities for future designs,’ Boydston points out.
The Manchester group also discovered how to tailor the polymer to favour certain mechanisms above others. ‘We just need to change the substituents,’ says De Bo. ‘If you add fluorine atoms, you stabilise the anion and thus the heterolytic pathway, if you remove them you favour the concerted mechanism and the formation of carbenes. The key is controlling the polarity of the carbon–carbon bond.’
Understanding how to control selectivity could allow chemists to customise mechanophores for specific applications. ‘Carbenes could catalyse self-healing reactions, promoting the formation of new bonds and new cross-links in damaged materials,’ explains De Bo. Boydston thinks that mechanism switching might eventually lead to materials that change their properties in response to external stimuli.
Potentially, these reactions could even improve polymer recyclability. ‘Hidden catalysts could accelerate degradation upon mechanical activation,’ suggests De Bo.
References
R Nixon and G De Bo, Nat. Chem., 2020, DOI: 10.1038/s41557-020-0509-1









No comments yet